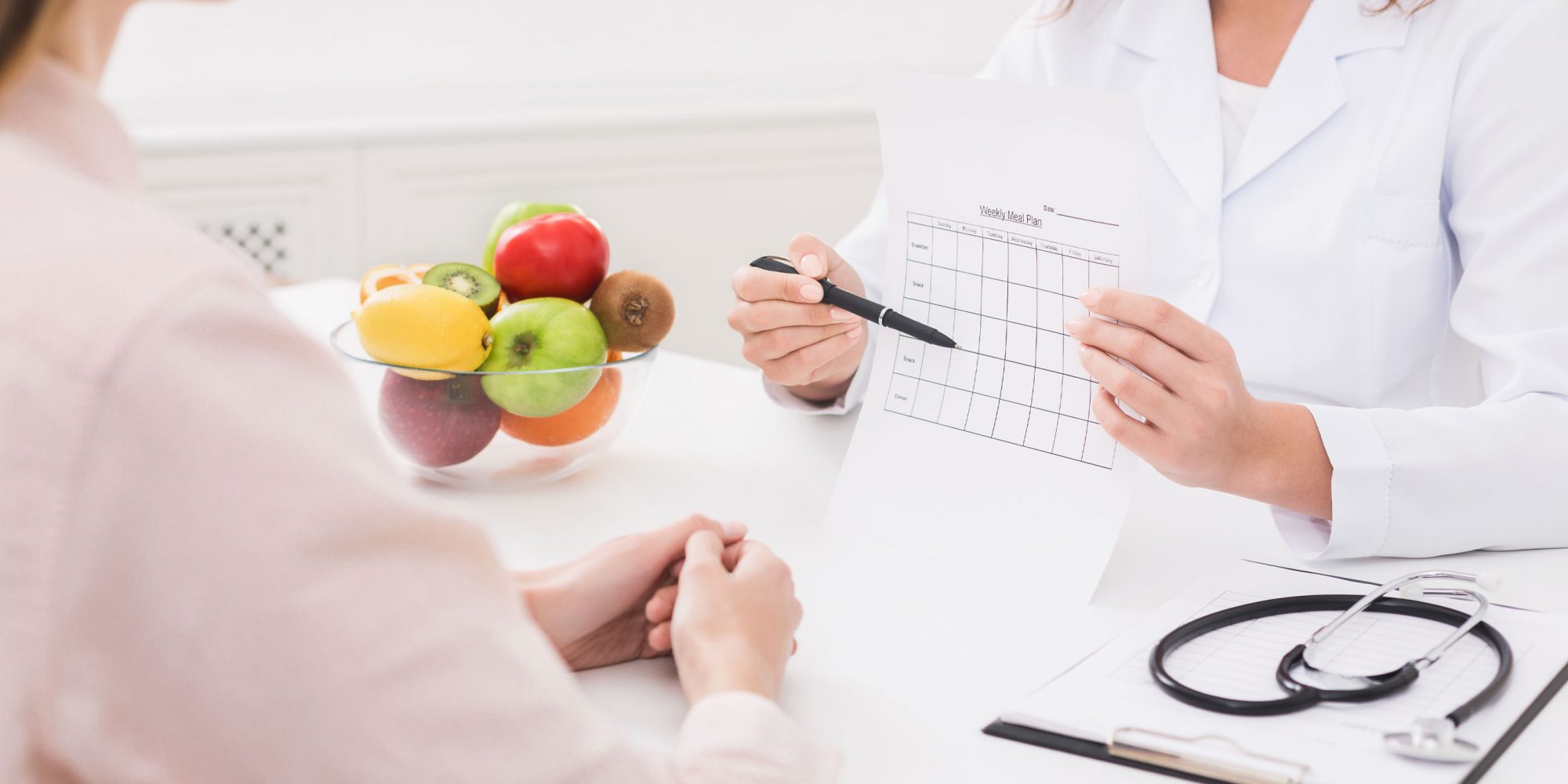

Recommending zero calorie Splenda® can help patients achieve and sustain their health goals. Switching from caloric sweeteners, like sugar, to Splenda helps your patients lose weight,1,2 manage diabetes and blood sugar levels,2 and live a healthier lifestyle.
Download any of the resources below today to help patients understand the benefits of using Splenda Brand Sweeteners.

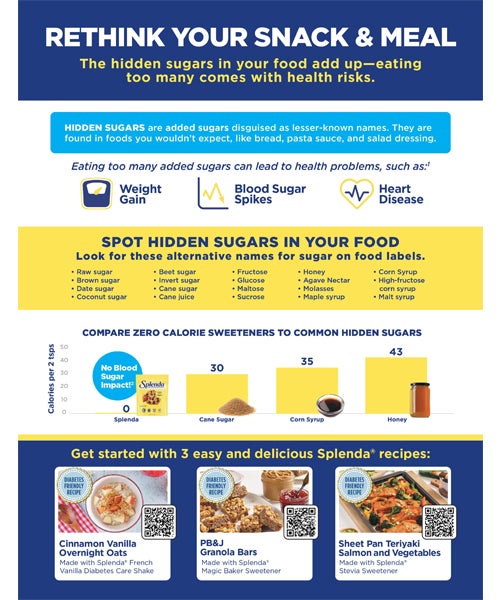














The safety and efficacy of low and zero calorie sweeteners (LNCS) have been researched for decades. This summary provides a selection of recent and well-designed scientific studies, articles and position statements in addition to a quick summary of the evaluation and regulatory review of LNCS in the U.S. and globally.
1 When used in place of sugar; Rogers PJ, Hogenkamp PS, de Graaf C, et al. (2016) Does low-energy sweetener consumption affect energy intake and body weight? A systematic review, including meta-analyses, of the evidence from human and animal studies. Int J of Obes 40(3), 381-394. 2 Johnston C, Stevens B, Foreyt J et al. (2013) The Role of Low-calorie Sweeteners in Diabetes. Eur Endocrinology 9(2); 96-98.